The Data Item Similarity report identifies items in your Knowledge Graph that are highly similar to each other based on how they are connected. This report is designed for data quality. It helps you detect:
Potential duplicates
Near-duplicates
Overlapping or redundant entities
Items that should be merged, linked, or clarified
Part of Knowledge Graph Health Reports
Step 1: Orphan Node Analysis – Find disconnected items
Step 2: Data Item Importance – Identify what matters most
Step 3: Data Item Similarity – Improve data quality and clarity
What This Report Shows
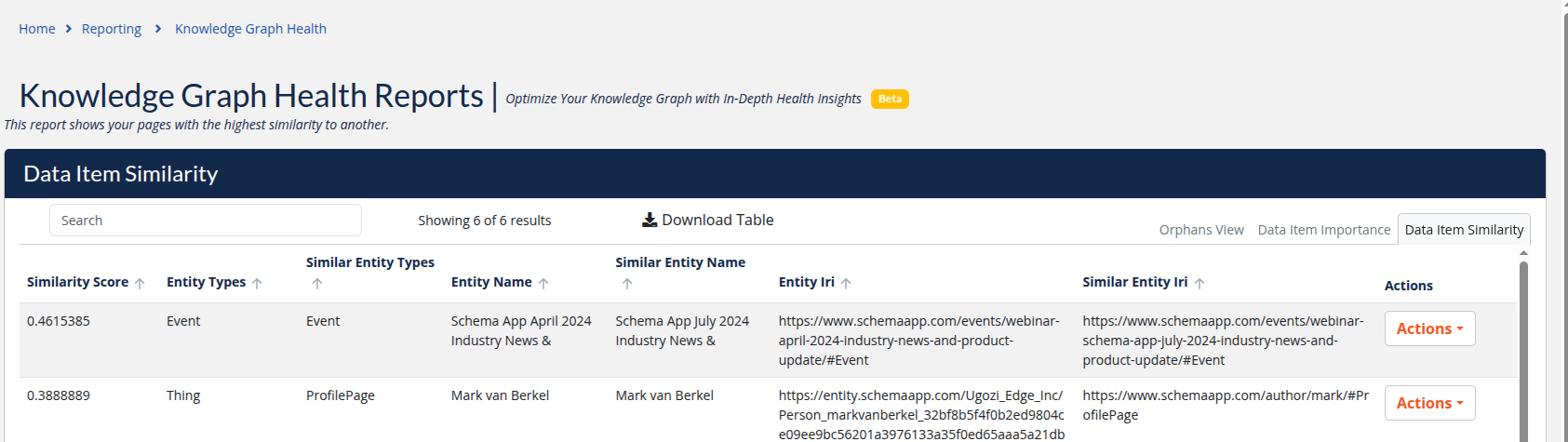
Each row represents a pair of items that the system has identified as being similar.
Similarity is determined by comparing:
The items’ relationships
Their position in the Knowledge Graph
The overlap in how they connect to other items
In short:
Two items are similar if they are connected to many of the same things.
How to Interpret the Results
The Data Item Similarity report identifies items that are structurally similar in the Knowledge Graph. Similarity here is based on shared relationships, not text matching or naming alone. Two items are considered similar if they:
Connect to many of the same entities or pages
Occupy similar positions in the graph
Understanding the similarity score
Similarity scores range from 0 to 1.
Use these ranges as guidance, not absolutes:
0.7 and above
Very high similarity
Often indicates duplicates or near-duplicates0.4 – 0.7
Meaningful overlap
Requires review to confirm intent0.3 – 0.4
Weak but notable similarity
Often caused by partial duplication or modeling gaps
Scores below this range are typically low-signal and may be ignored.
The key question to ask
“Are these two items intended to represent the same real-world thing?”
If yes:
You likely have duplication
Consolidation or merging would strengthen the Knowledge Graph
If no:
The items may be insufficiently differentiated
They likely need clearer relationships, types, or contextual properties
What actions should you take?
For each similar pair, choose one:
Merge
If both items represent the same thingDifferentiate
If both items are valid but distinct
Add clearer relationships, properties, or naming to reduce overlapAccept intentionally
Some similarity is expected (e.g., recurring events, related profiles)
Why this matters
Unintended similarity can:
Dilute entity authority
Create ambiguity in downstream analysis
Reduce the clarity and precision of your Knowledge Graph
This report is about precision and clarity, not volume reduction.
How to Read the Report
Each row shows one item and its most similar counterpart.
Columns Explained
Similarity Score
A score between 0 and 1 indicating how similar the two items are.
Higher score = more overlap in relationships
Scores above ~0.3 typically indicate meaningful similarity
Scores closer to 1 suggest near-duplicates
This is a relative signal, not a definitive verdict.
Entity Types
The type of the primary item.
Examples:
EventPersonThingProfilePage
Similar Entity Types
The type of the matched item.
Matching types often indicate duplication.
Mismatched types can signal modeling or authoring issues.
Entity Name
The name of the primary item.
Similar Entity Name
The name of the most similar item.
This is often where issues become immediately obvious (e.g. two events with different dates but identical structure).
Entity IRI
The unique identifier of the primary item.
Similar Entity IRI
The unique identifier of the similar item.
These confirm that the system is comparing distinct graph items, not aliases.
Actions
Contextual actions you can take, such as:
Reviewing the items side by side
Editing or consolidating entities
Correcting relationships or types
Why Similarity Matters for Data Quality
High similarity usually indicates one of the following:
1. Duplicate Entities
Two separate items represent the same real-world thing.
Example:
Two versions of the same event
Multiple entities for the same person
2. Fragmented Modeling
The same concept is split across multiple items, each partially connected.
This weakens:
Entity authority
Graph clarity
Downstream insights
3. Legitimate Variants (But Needs Clarity)
Some similar items are valid but require:
Clear differentiation
Stronger contextual relationships
More precise naming or typing
What You Should Do Next
For each similar pair, decide one of three actions:
1. Merge
If both items represent the same real-world thing:
Consolidate into a single item
Preserve the best relationships and properties
Remove or redirect the duplicate
2. Differentiate
If both items are valid but distinct:
Strengthen distinguishing relationships
Improve names or descriptions
Add clarifying properties (dates, roles, context)
3. Ignore (Intentionally)
Some similarity is expected (e.g. recurring events or series).
In these cases:
Confirm the similarity is intentional
No action may be required
Best Practices
Review this report after resolving orphan nodes
Focus first on high similarity scores
Prioritize items with:
The same type
Very similar names
High importance in the graph
Use this report regularly as part of graph hygiene
How This Fits with Other Health Reports
Orphan Node Analysis
Finds disconnected items.Data Item Importance
Identifies which items matter most.Data Item Similarity (this page)
Ensures important items are clean, distinct, and intentional.
Together, these reports help you move from having a Knowledge Graph to maintaining a high-quality one.
Summary
The Data Item Similarity report helps you:
Detect duplicates and near-duplicates
Improve modeling precision
Strengthen Knowledge Graph integrity
If importance tells you what matters, similarity tells you where quality is at risk.
Was this article helpful?
That’s Great!
Thank you for your feedback
Sorry! We couldn't be helpful
Thank you for your feedback
Feedback sent
We appreciate your effort and will try to fix the article